Particularly during the last years, the use of electric scooters has considerably increased in the main European cities, undoubtedly with the aim and benefit of reducing air pollution, reduce traffic congestion and replace the use of private vehicles for short distances.
Despite of all the benefits, the introduction of electric scooters has also created various challenges in a number of cities where they operate. We have seen a number of operators who have introduced this new method of transport without prior consultation with the local authorities or the regulatory officials in terms of security. This situation has created disagreement on the usage of public spaces, road security and traffic management.
The number of e scooters which have been introduced in various cities is dependent on the number of operators using the service. If we had to give a random look to various European cities, we would find that a number of the e scooters vary from a couple of hundreds to thousands. Hereunder are some examples.
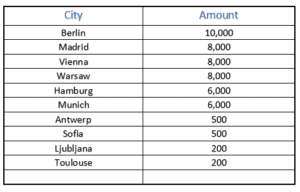
Fleet size vs public spaces
As one could notice, there is a noticeable difference between one city and another. The influx of these e scooters has come to a point where certain cities had to act and introduce an operational regulatory framework and Malta is no exception. The infrastructure, the actual use of e scooters and the citizens’ attitude towards them are the key factors which make e scooters’ usage and regulatory enforcement somehow different from one city to the other.
The city of Budapest could be taken as an example of how diligently the e scooter process was introduced; the city adopted an initial scheme of 200 e scooters in a prominent zone in order to have first-hand information and data before actually legislating the regulatory process. This, has actually given them the chance to process in a factual way all the data gathered during this eight-week trial. This trial period has put at the forefront the need for a mitigation process on issues related to public spaces, where these scooters could be used or not. This led to structured discussions with the operator which alternatively led the public to seamlessly embrace this alternative way of transport.

During a study carried out during the last two years resulted that 16 out 19 cities which were under research identified common issues to Malta related to e scooters, namely:
- the attitude of electric scooters’ users
- parking spaces and the way e scooters are carelessly abandoned after use
- driving speed
Certain cities had to introduce different measures for various zones including historical heritage sites, public parks and other touristic sites; this was intended to segregate other means of transport including those going on foot. Besides, these measures also safeguarded historical sites and touristic zones from unpleasant situations where electric scooters are carelessly and haphazardly left along the way. Consequently, some cities have set up designated areas from where those using the e scooters could commence and eventually end their trip without leaving their scooter out and about on pavements or public gardens. These regulatory measures also cater for tother challenges which so far have not been mentioned namely,
- The use of e scooters on pavements
- Lack of proper framework which addresses the same challenges
- Wreck less driving
- Damage to parked vehicles
- Electric scooters’ drunken users
- Multiple people riding same e scooter
- Lack of suitable insurance cover
- Abandoned e scooters (in puddles and rivers)
Scooting zones
It is somehow crucial that whenever possible there should be a segregation of the various means of available transport methods. It does not make sense that e scooters are operated in pedestrian zones, foot paths or pavements; this takes on board the issue of speed when it comes to these scooters. A pedestrian walking at a speed of four kilometres per hour iwould be severely injured if he gets hit by a scooter with a speed of between 16 to 20 kilometres an hour. This all depends on the individual’s stature because of a senior citizen is hit with that velocity he would surely end up dead since his body would not endure such impact.
Certain cities are turning to technology to try to reduce accidents and injuries among riders and pedestrians with the use of inbuilt e scooters sensors, the latter detecting impact and automatically reducing speed. In case of the lack of human intervention during the scooter’s operation the sensor would automatically stop the e scooter. This also applies to heavily pedestrianised areas, city squares and streets with heavy traffic flows.
Sanctions from certain sites or parks happen through geographical restrictions; this means that when a scooter reaches the designated zone it would automatically trigger the GPS and the latter would stop the scooter from entering that particular zone. This technical intervention does not require human resources to ensure its enforcement. As this cost onus is burdened by the operator the city would not incur extra expenses related to the deployment of human resources needed for this enforcement to take place.
Continuous dialogue
However, when putting aside the disadvantages, one could easily outline from a financial perspective a series of environmental benefits from this sustainable transport service. Those cities who reaped the maximum benefit of this alternative means of transport are those who managed to pool all the stakeholders for this initiative to successfully be implemented. This was done through continuous meetings amongst all those involved and the exchange of gathered data. This mechanism has brought together on the table a number of factors namely: public debates, operators who recognize their own responsibilities, the establishment of the maximum numbers of scooters per identified zone, the adoption of an open-minded approach and the ability for the modification of old habits along with total coordination with those involved.
Should a city ensure an efficient, safe and inclusive service it must take into consideration the number of required scooters needed to cater for that particular place. This planning is of utmost importance to the operators themselves since the granting of licences to a larger number of operators would be unhealthy to that same city if the latter could be well maintained with a reduced number of operators.
Therefore, it is crucial that the right mechanism should be in place to ensure:
- What should be the maximum number of scooters and the capacity of each operator
- The cost and validity period of each e scooter licence
- Type of needed insurance cover
- Proper structuring of people’s complaints
- Operators’ obligations towards stipulated timeframes for complaints’ replies
- A round the clock point of contact for any assistance needed by the Municipality or the respective locality council
- A penalty structure mechanism in place which incorporates an implementation and fee collection process
The social impact
From a social perspective, this industry which is somehow ever growing needs to have a recruitment framework. These operators would need to employ a number of back office and on the ground employees to assist in the handling of these scooters along with the necessary repairs from time to time. Hence, there needs to be a regulatory framework in place to ensure that these employees won’t be legally abused. What comes to mind are the employees within the food delivery sector who definitely do not have the best of employment conditions; one has to ensure that no sector would ever adopt such practices.
Such monitoring is carried out by various cities and its findings are usually discussed in various meetings which are regularly held between the stakeholders and the operators themselves.
The environmental impact
E scooters usage definitely carries out as a direct or indirect environmental impact which could be significant without the correct measures. Studies which have been caried out highlight the direct impact these could have on the environment through their regular usage, rental life span, the process and practices of how these e scooters are handled by the operator and the production material used and their weight.
Further studies which have been carried out show the impact e scooter rentals had on others methods of transport. One clear example is Brussels where e scooters replaced 26% of private vehicles, 29.2%of public transport trips and 40% of bicycle and pedestrian journeys.
By swapping the use of private vehicles and public transport usage to e scooter usage, the latter also removed the health benefits that come from walking or cycling these journeys.
Hence, certain cities are encouraging e scooter operators to focus on the impact reduction these scooters could have in these central areas. This is achieved by the operators themselves considering the purchase of scooters with a longer operative lifespan, invest in proper vehicles which handle e scooter collection and distribution in these zones and ensure that their fleet is made up of e scooters made of recyclable material while ensuring that the scooters are equipped with higher capacity and long-lasting batteries which require minimal charging time and have zero emissions. All of these factors would place the operator in an advantageous position to incur a preferential licence fee since he would be positively contributing towards the environment.
Street security
According to researched data, e scooters pose higher risks to street security with accident rate for e scooters being nearly seven times higher than bicycles; this situation poses a higher administrative burden on the administration team of the Local Councils.
Many cities have very clear established safeguards and guidelines for whoever wants to operate this kind of transportation. These should factor in reduced impact on traffic accidents, the prohibition of drink riding, smoking, and eating as all of these collectively allow the passenger to be fully focused.
In this contest, during a study which was carried out in the capital city of Denmark showed how 36% of those involved in accidents were under the influence of either alcohol or drugs with one third of the incidents happening between 11o’clock at night and 7 in the morning. This factor could lead to the suspension of service in certain zones and between certain periods.
One is good to know that the results of this study showed that nearly 9% of those involved in these incidents were pedestrians, three quarters of which were vulnerable members aged from new born to 14 years, sixty-year-old citizens and older. A collection of similar data could help the adoption of certain measures for
- Educational campaigns carried out for specific age groups
- Minimum age for driving scooters depending on zones and time being driven
- Limitation of one person per scooter
- Obligatory use of helmets
- Calls for e scooter riders to be banned from using their mobile phones while driving
- Access rates to be analysed based on distance rather than time
All of this clearly shows the importance of a constant dialogue between all stakeholders for such measures to be equally supported by all parties and be implemented in the fastest and most efficient manner.
Infrastructure
Undoubtedly, the most important factor in all this remains the infrastructure. After the pandemic crisis the want for more open public spaces and pedestrian zones has increased. For a couple of months during the pandemic we have witnessed public squares and streets completely empty from vehicles where everyone had the chance to enjoy whatever previously could not be much appreciated.
From an infrastructure perspective we have to keep in mind that these e scooters have different characteristics from those related to vehicles. Electric scooters with small wheels are less comfortable to ride since smaller wheels tend to dip into potholes and unlevelled road surfaces, thus the impact is much stronger than a vehicle.
On the other hand their use on pavements is quite chaotic. Hence it is crucial that an adequate infrastructure for this relatively new means of transport which does not only see the need for the proper segregation of routes but also a smoother surface and more e scooter usage friendly systems. It is thus of utmost importance that e scooters would be equipped with a good GPS system so that when the approach pedestrian areas they would automatically reduce speed.
Parking spaces for e scooters is another crucial aspect of the infrastructure. Like many other countries it is imperative that every so often one would find allocated spaces where these e scooters would be parked and charged in an organised manner; contrary to this we experience scattered e scooters haphazardly left around.
Universal docking and charging stations which would function and cater for all major electric scooters are of primary importance as these would create aesthetic soreness while they unnecessarily occupy public land.

What our country is going through
Way back in 2018 we have started experiencing an increase in this mode of transport which kept on increasing in 2019; during September of the same year the Transport Authority has called for a consultation process to better regulate the usage of electric scooters.
We have always believed and documented that despite the usage of the electric scooters requires less effort than driving a bike and make use of public transport, their usage will somehow has an impact on other residents. It would impact the residents’ quality of life when it comes to the use of public and open spaces and when one considers the access to open spaces for persons with special needs.
We believed and anticipated that electric scooters usage will continue to destroy the few remaining open spaces and walking zones within our villages. Since their usage was not allowed in tunnels and main roads has thus purely left their usage in local areas. That is the reason why we insisted on deeper discussions with the Association of Local Councils and the Local Councils themselves to ensure that was written earlier and what was happening beyond our shores could likewise be applied to our country.
The infrastructure investment which occurred in Malta and which was long overdue was mainly concentrated on the use of vehicles; this has increased the need to work more on alternative transport methods with a longer vision. Consequently, that is why the use of electric scooters on pavements should never be the subject for discussion. Walking should remain the most sustainable way of transportation and should we keep on taking over the little available spaces left it would leave us no further walking space; indirectly we would be encouraging our residents to keep on making use of their private vehicles.
The dedicated use of segregated parking spaces for bikes and scooters is the most efficient manner on how this alternative transport method is utilized.
One has to differentiate between the private and commercial use of these electric scooters
One might ask:
- Should an individual making private use of electric scooters pay the same licence fee similar to companies occupying public space? Private e scooters users would usually store their electric scooter either at home or at their place of work upon arriving at their respective destination and thus occupy no public space; hence shouldn’t these private users be incentivized for not creating an inconvenience? Whereas private users would be storing their scooter in their own property commercial operators would be using limited public spaces.
- If electric scooters usage is designated to local streets and areas, shouldn’t Local Councils be the owners of these licences who would then decide on the quantity of issued licences pertaining to and in line with the rules and regulations of their respective locality.
- Should there be an accessible data base for these electric scooters with information related to where they are being mostly used and their frequency?
- Should the Local Council have the necessary authority to retrieve the licence of any operator if the latter would not abide by its obligations?
- Should there be a screening process prior to the operative licence renewal of how coherent was the operator in line with its obligations, what accidents were caused and what was customers’ overall behaviour (thus why it is necessary that the operator should have the authority to charge his customers on negligence)
- Should the operating licence fluctuate in line with the expense needed for better enforcement?
- Should there be a revision of the age limit for electric scooter usage?
These and other questions are to be the basis for discussion following the three-year period following the introduction of the National policy. Following lessons learnt, the time has come for a more mature and open discussion. We would now be in a position to update and improve our framework in this sector while minimizing the challenges.
An improved and structured regulatory framework would be beneficial not just for the residents but most of all to the environment, traffic management and the operators themselves.
Mario Fava
President